What is the time to odontogenic sinusitis (ODS) resolution after primary dental treatment and endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) based on symptom, the 22-item sinonasal outcome test (SNOT-22), and endoscopic outcomes?
BOTTOM LINE
For symptomatic ODS, primary ESS resulted in faster resolution of SNOT-22, sinusitis symptoms, and endoscopic findings in ODS patients compared with primary dental treatment.
Explore This Issue
September 2019Background: Various odontogenic pathologies can cause ODS, including pulpitis, periapical lesions (cysts, abscesses, granulomas), periodontitis, oroantral fistula (OAF), or dental treatment-related sinus foreign bodies, all of which make it challenging to distinguish ODS from sinogenic sinusitis. Published series report excellent success rates with dental treatment, endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS), or both.
Study design: Prospective cohort study of 37 symptomatic ODS patients who failed medical management and selected primary dental treatment (11) or ESS (26).
Setting: Department of Otolaryngology, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, Mich.
Synopsis: ESS patients had both periapical disease and extraction-related temporary OAFs, whereas all dental patients had periapical disease. All patients received 2.6 ± 1.6 oral antibiotics before undergoing treatment. Dental patients were followed for an average of 77.5 ± 66.5 days after treatment. The mean pretreatment SNOT-22 score was 32.6, and mean SNOT-22 change post-treatment was 0 ± 14.8. Four patients improved symptomatically, endoscopically, and by SNOT-22 during follow-up. Seven failed to improve, with five then undergoing ESS. No complications occurred. ESS patients were followed for an average of 146.6 ± 195 days postoperatively. The mean preoperative SNOT-22 score was 40.2, and mean SNOT-22 change postoperatively was −28.7 ± 24.8, significantly greater than that of dental patients. After ESS and before subsequent dental treatment, all 26 patients experienced sinusitis resolution without recurrence (symptoms, endoscopic findings, and clinically significant SNOT-22 reductions). No complications occurred during or after ESS, and no revision ESS was required.
Limitations included a small sample size, especially for dental patients, the combination of periapical disease and temporary OAF patients in the ESS outcomes analysis, and potential patient treatment selection bias.
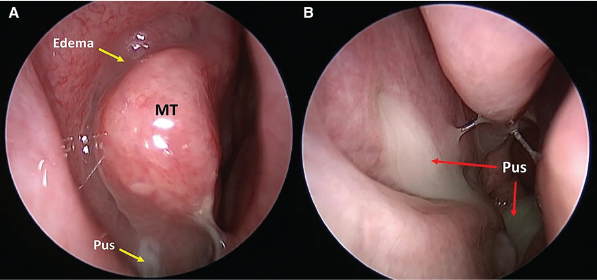
Representative nasal endoscopy findings of the middle meatus. (A) Edema and mucopurulence in the right middle meatus. (B) Purulence draining from an accessory maxillary sinus ostium through the right middle meatus and into the nasopharynx.
© 2019 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc.
Citation: Craig JR, McHugh CI, Griggs ZH, Peterson EI. Optimal timing of endoscopic sinus surgery for odontogenic sinusitis. Laryngoscope. 2019;129:1976–1983.