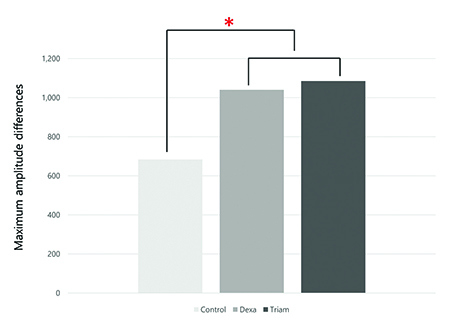
Figure 2: The mean maximum amplitude differences of the Control group, Dexa group, and Triam group (*p < 0.05).
A significant difference in the mean maximum amplitude was observed between groups (p < 0.05). Post hoc analysis indicated that the mean maximum amplitude was significantly higher in both the Dexa group (1040 ± 128 µm) and the Triam group (1085 ± 129 µm) than in the control group (684 ± 181 µm) (p < 0.05) (Fig. 2). No significant differences were found between the treatment groups.
Explore This Issue
May 2025Histological Data
Significant differences were noted in both the mean CD ratio and CSA among the groups (p < 0.05). In post hoc analysis, the mean CD ratio was significantly higher in controls (43.5 ± 7.2%) than in the other groups (p < 0.05). No significant differences were noted between the treatment groups. The normalized mean CSA score of the Triam group was significantly lower than that of the controls (p < 0.05). No significant intergroup differences were observed between other groups.
Real-Time PCR of ECM Genes
Real-time PCR analysis showed significant increases in HAS2 gene expression in the treatment group compared with controls (p < 0.05). Conversely, the expression levels of the gene encoding collagen type IV were notably lower in the treatment group (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSION
Corticosteroid injection notably increased the levels of mRNAs encoding HAS2 and MMP-9. From a histological perspective, the CD ratio was lower in the treatment groups, and there was a significant improvement in MAD. This indicates that corticosteroid injection substantially enhanced vocal fold vibration. We conclude that corticosteroid injection acts as a preventive measure against vocal fold scarring by promoting wound remodeling and reducing fibrogenesis. Additionally, the observed atrophy in triamcinolone-injected vocal folds underscores a potential adverse effect of glucocorticoids on vocal fold tissue, warranting further investigation.
Leave a Reply