When deciding whether to perform tracheotomies during COVID-19 required laryngologists to balance important medical and resource needs with the possibly grave infection risks to medical personnel.


When deciding whether to perform tracheotomies during COVID-19 required laryngologists to balance important medical and resource needs with the possibly grave infection risks to medical personnel.
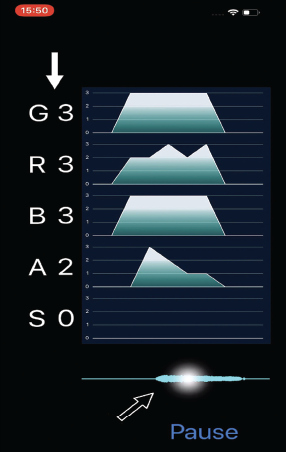
The purpose of this research is to facilitate the use of a deep-learning architecture with the GRBAS scale in clinical practice.
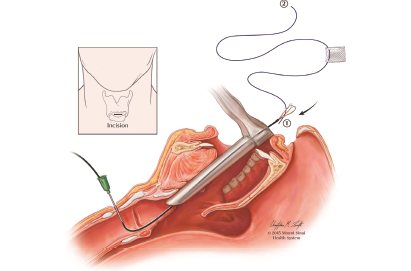
Instead of removing the keel in the operating room under general anesthesia, this can be done in the office with topical anesthesia.
A look at the factors and complications associated with prolonged inpatient length of stay in patients who receive total laryngectomy.

Pulmonary function testing is useful in the evaluation and management of subglottic stenosis because it provides a precise and objective functional assessment of obstruction.
Hypopharyngeal-proximal reflux episodes occur less frequently than gastroesophageal reflux disease episodes after meals and at night, and future therapies for LPR patients should take the HEMII-pH profile into consideration.
The American Thyroid Association published its latest update on management guidelines of thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer. Here’s how the update changes patient care.
What are the predictors of airway collapse and the need for airway intervention in adult epiglottitis?
New study uses machine learning on ultrasound images of thyroid nodules to predict risk of malignancy
What is the extent of airway improvement and voice quality in patients with bilateral vocal fold paralysis (BVFP) who underwent selective laryngeal reinnervation surgery?