Explore This Issue
September 2011Fat grafts have been used to repair the aging face for about two decades, but recently, surgeons have been using grafts to repair more extensive facial deformities caused by injury, illness or congenital abnormalities. Success, they said in interviews with ENT Today, depends on proper patient selection, matching the fat graft to defects that are most amenable to repair with fat injections and an understanding of the biology of the graft and how it reacts with surrounding facial structures.
Samuel M. Lam, MD, a plastic surgeon in Plano, Texas, and co-author of “Complementary Fat Grafting” [Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006], told ENT Today that although fat transfers for the aging face can yield impressive results, the nature of grafts means inherent risks that limit their potential in the repair of more extensive soft tissue trauma.
“Fat is a live graft; it’s not a bioinert substance like Restylane or other injectable filler products. So it carries with it a certain level of morbidity that we don’t always appreciate,” Dr. Lam said. He noted, for example, that fat grafts can change in volume and shape as a result of weight loss or weight gain. This makes fat grafts a poor choice in the younger, metabolically active patient who has experienced a traumatic injury or extensive surgical excision and requires a large area of correction.
“I’ve seen these patients earlier in my practice. They gain 20 to 30 pounds after fat transfer, and their faces look bloated and even distorted,” he said.
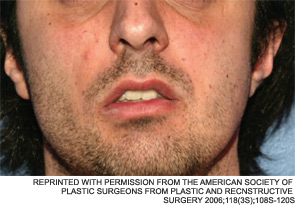
Dr. Lam said that such suboptimal outcomes are certainly not limited to his own experience. He knows of cases in other practices where problems arose from using fat grafts in metabolically active patients. In one such case, which he detailed in a paper on the “do’s and don’ts” of fat transfers for soft tissue trauma (Facial Plast Surg. 2010;26(6):488-493), a colleague employed a fat transfer to treat a young woman with a unilateral mandibular defect. “About 18 months after the procedure,” Dr. Lam said, “the graft had attracted a blood supply and had grown to the point where she developed a very noticeable protuberant deformity—it actually looked like a tumor.”
A better choice in such cases, he noted, would be to use a removable alloplastic material such as silicone to correct the defect “as long as there is enough soft tissue coverage to ensure that the implant will not be exposed.”
Leave a Reply