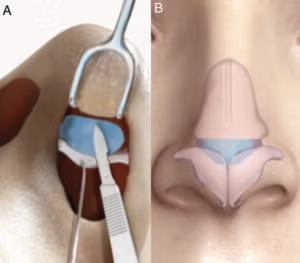
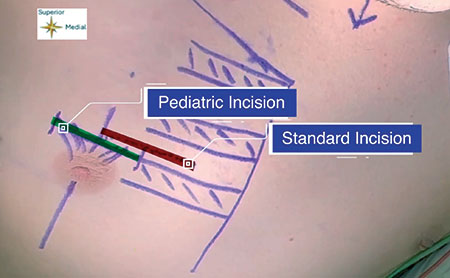
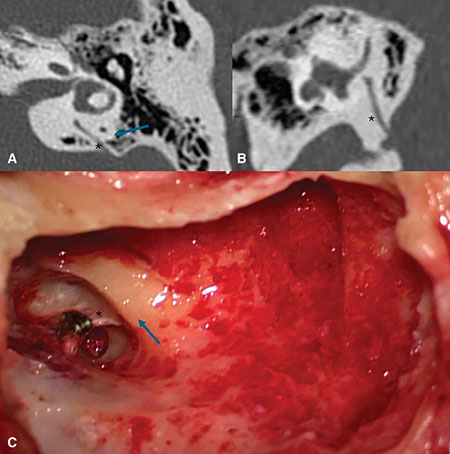
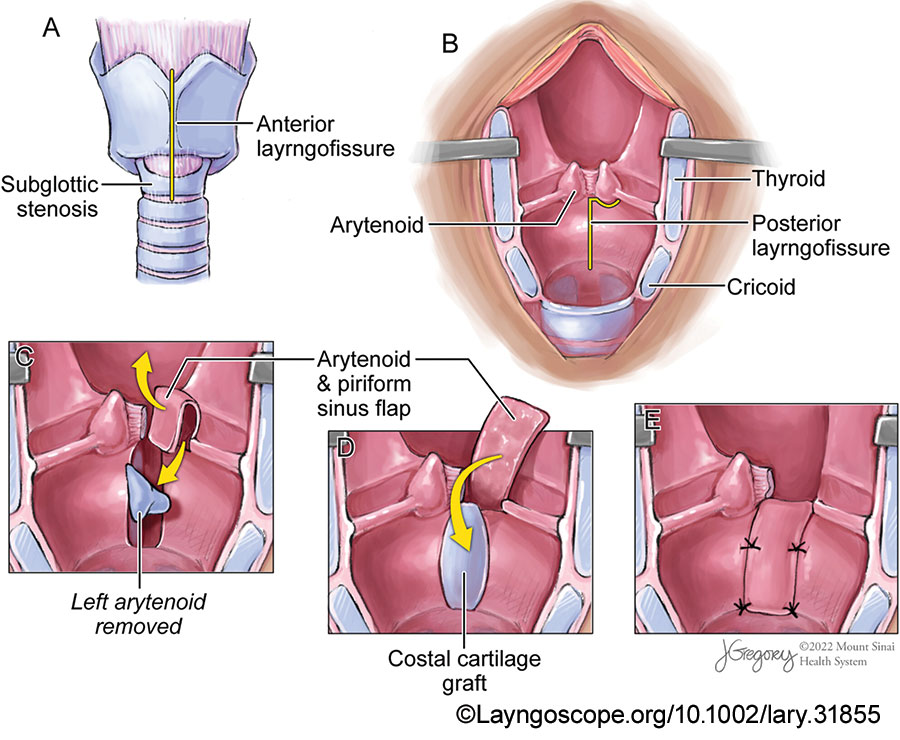
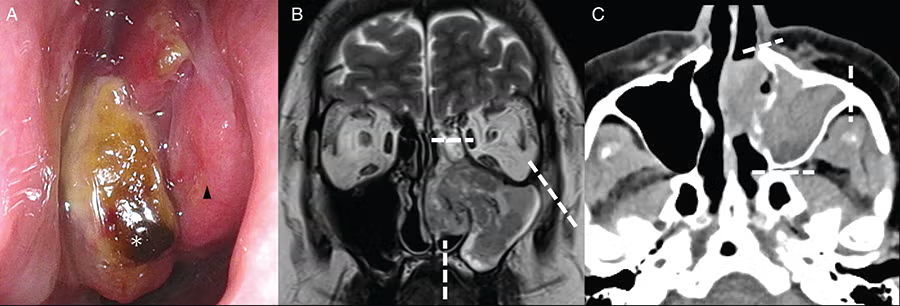
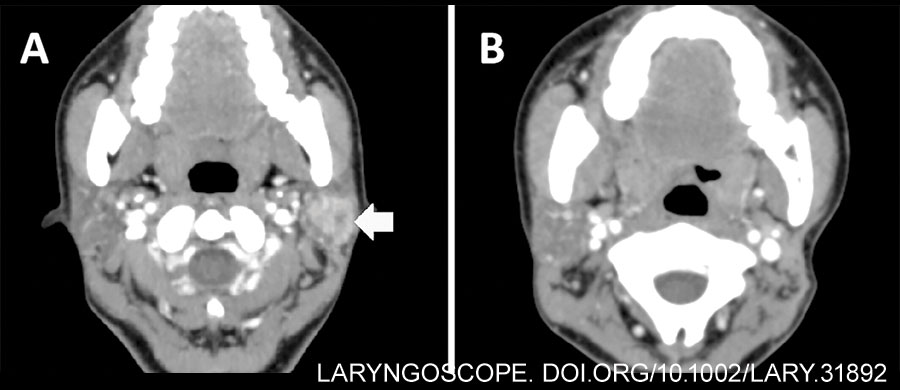
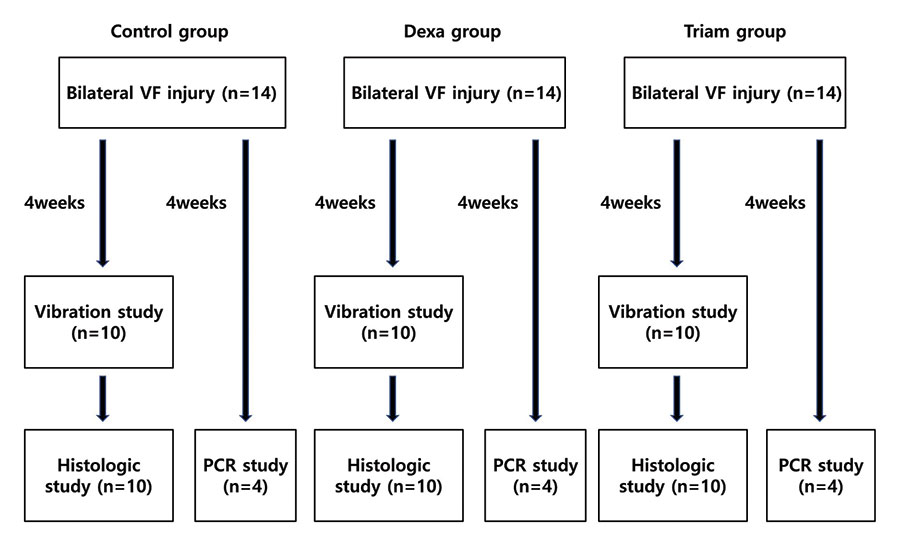
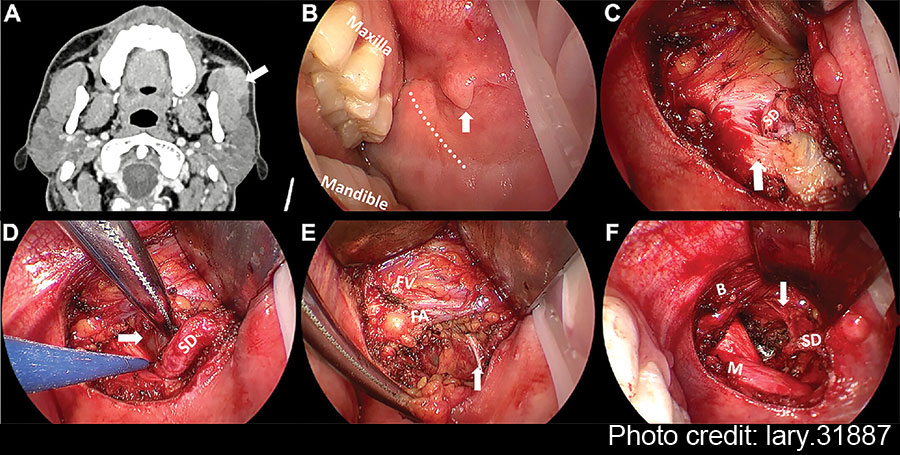
The butterfly graft (BFG) is a surgical technique used to treat nasal airway obstruction by reconstructing the internal nasal valve, but it can lead to external nasal contour irregularities. This study evaluates a secondary contouring procedure designed to address these irregularities while preserving nasal function and improving patient satisfaction.