This study describes the successful use of a hybrid resection and laryngotracheoplasty procedure that maximizes airway luminal patency in adults with successful decannulation.
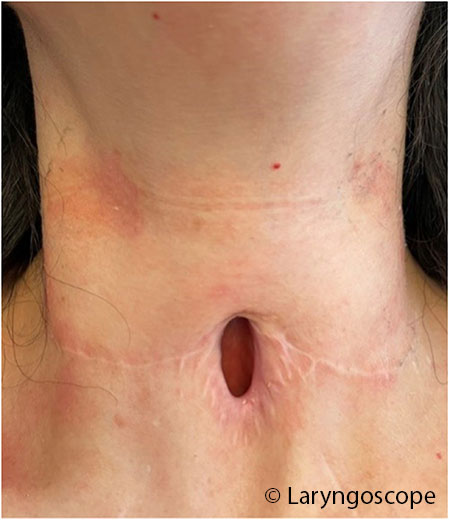

This study describes the successful use of a hybrid resection and laryngotracheoplasty procedure that maximizes airway luminal patency in adults with successful decannulation.
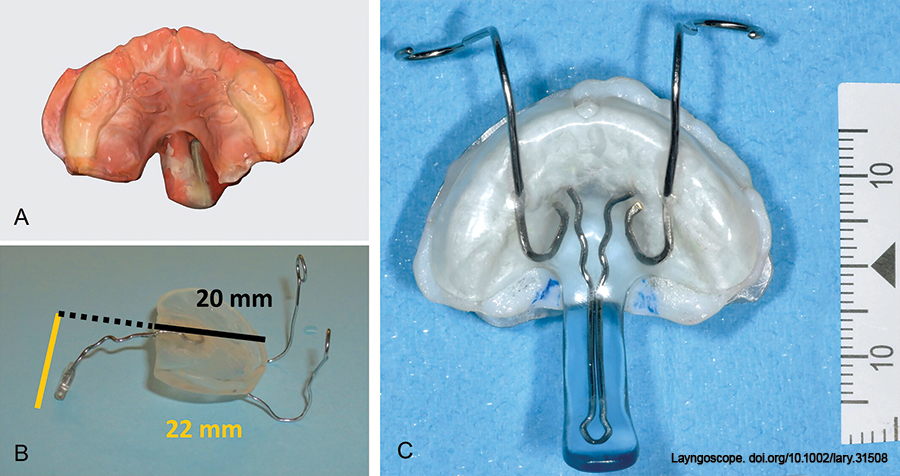
Pierre Robin sequence (PRS) has an estimated prevalence of one in 10,000 births and is characterized by micrognathia and glossoptosis leading to upper airway compromise. As airway obstruction can be life-threatening, immediate recognition and treatment are vital.
Onyx is a safe and effective embolic agent used in the treatment paradigm of jna. This study offers a tandem approach that combines tae with dpe and onyx to limit blood loss and facilitate safe resection.
A safe technique for transnasal endoscopic drainage of upper parapharyngeal abscesses.
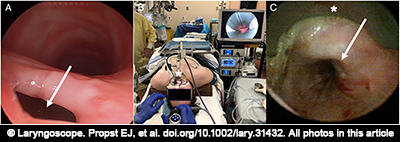
This protocol describes the method for creating 3D-printed trachea models for use in high-fidelity simulation-based training and advanced surgical planning for pediatric patients undergoing slide tracheoplasty.
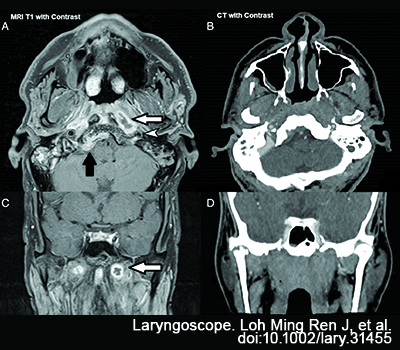
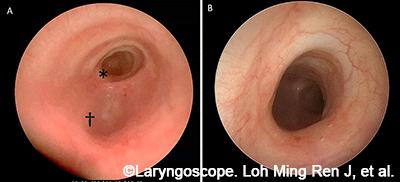
This study is about a patient for whom suspension microesophagoscopy was performed and describes how this approach allowed for improved management.
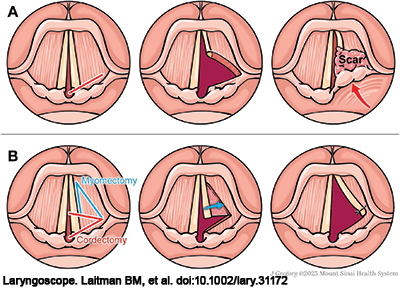
Currently, Bilateral Vocal Fold Immobility (BVCP) is often treated by transoral CO2 laser-assisted transverse cordotomy. Still, this procedure can lead to subsequent scarring at the wound bed, resulting in re-narrowing of the airway and poor voice. Transverse cordotomy with thyroarytenoid myectomy may promote faster healing and may limit scarring and restenosis.
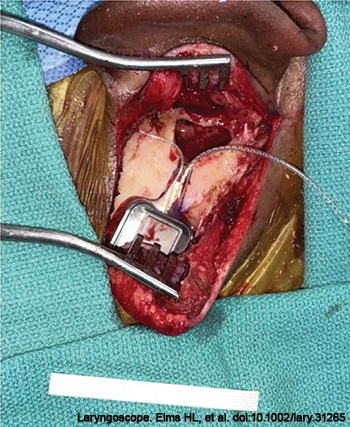
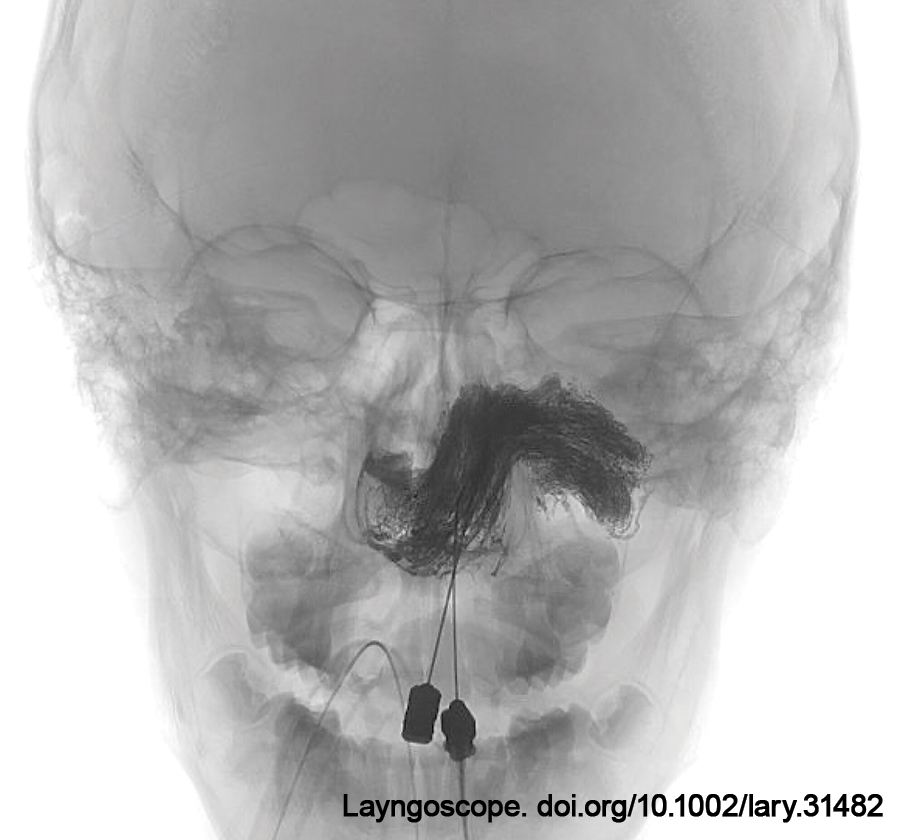
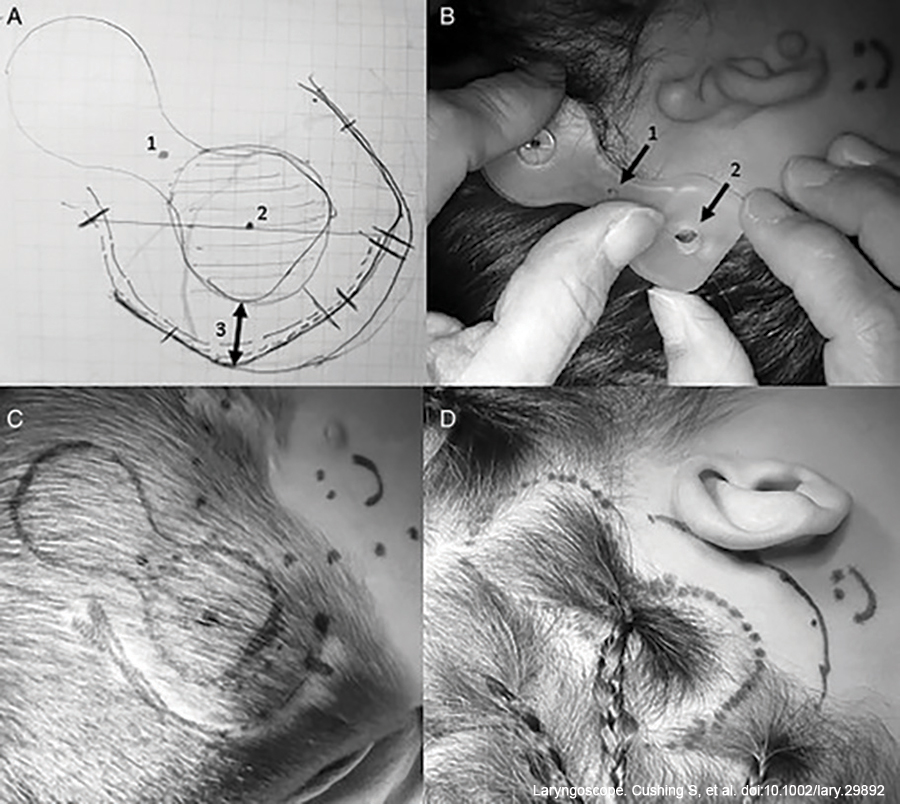
In this study, we describe a time-saving modification of a bony-bed technique that utilizes screw-fixated Mersilene cervical cerclage suture, originally designed for treatment of uterine cervical insufficiency, as a simple, quick, and effective method for tie-down receiver/stimulator fixation.
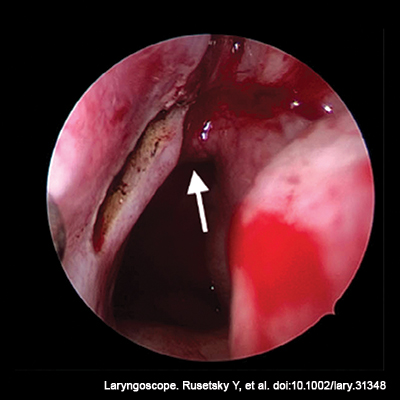
Posterior septal artery flap for endoscopic repair of large nasal septal perforation aims to demonstrate the effectiveness of the endoscopic repair of large SPS utilizing flap pedicled with branches of PSA.
The osseointegrated steady state implant 2 (OSIA2) system was developed to provide hearing through bone conduction while avoiding complications previously reported in children using percutaneous devices.