Is there a role for bedside biopsy in the evaluation of acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis?


Is there a role for bedside biopsy in the evaluation of acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis?
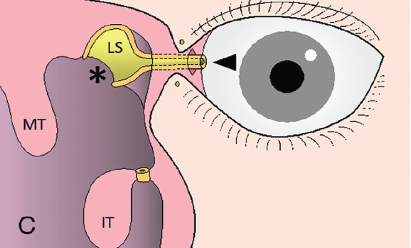
We introduce a novel method, conjunctivoductivo-dacryocystorhinostomy, for anastomosis of the conjunctiva and nasolacrimal duct without leaving any facial scars or foreign bodies in semi-permanent detention.
A look at what neurodegenerative changes can be observed with MRI in patients with olfactory impairment and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or dementia.
Olfactory dysfunction (OD) presence does not seem to be useful in identifying subjects at risk for being COVID-19 super spreaders.

The endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach is an effective technique commonly utilized for resection of sellar and parasellar lesions.
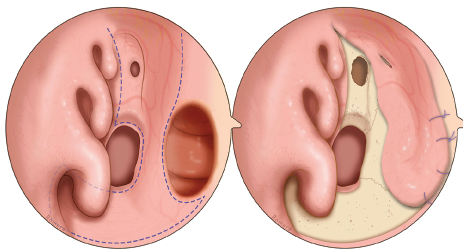
The objective of this study is to describe step by step an innovative technique to repair large septal perforations with a pure endoscopic extended AEA flap.
Nasal and nasopharyngeal lavages appear to be well tolerated and highly reliable in detecting SARS-CoV-2.
A look at the impact of novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) on the risk of epistaxis and its severity.

The current level 1 evidence does not support the routine use of oral antibiotics postoperatively.
Minority demographic groups are significantly underrepresented in chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) clilnical trials.