Placement of the sensing lead can be challenging in obese and Down syndrome patients. This article presents an alteration in technique for its placement in these patient populations.
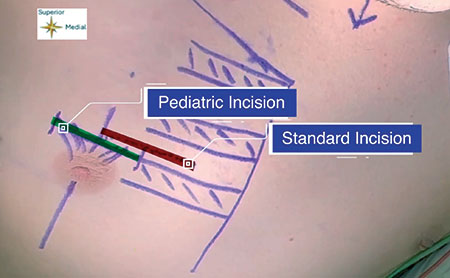

Placement of the sensing lead can be challenging in obese and Down syndrome patients. This article presents an alteration in technique for its placement in these patient populations.

When it comes to drug therapy most of the recent buzz has been triggered by data on tirzepatide released at the American Diabetes Association 84th Scientific Sessions, suggesting that the drug may obviate the need for continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in nearly half of OSA patients.
Identifying and managing sensing lead malfunction in upper airway stimulation devices using the Inspire Medical Systems’ upper airway stimulation (UAS) device to treat patients with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), to necessitate revision surgery.
Ansa Cervicalis Stimulation could become a viable ancillary respiratory neurostimulation (RNS) strategy for patients with insufficient responses to hypoglossal nerve stimulation (HNS).

At least two new hypoglossal nerve stimulation (HNS) devices are being evaluated in clinical trials, and more are in development.
Upper airway stimulation is a treatment used to address OSA by electrically stimulating select levels of the hypoglossal nerve to induce contraction of the genioglossus muscle and enlarge airways.

Treatment for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) continues to advance, from the increasingly sophisticated realm of wearables to new techniques for implantable devices.
Hypoglossal nerve stimulator implantation in an ambulatory surgical center is safe and is more efficient than in an HOPD and may also be more cost-effective.
Among veterans with OSA, Black race was associated with reduced PAP adherence, suggesting health inequality among Black individuals in the treatment of OSA.
This interval update from the ADHERE registry outcomes demonstrates efficacy, safety, and high adherence rates for UAS therapy.