Endoscopic anterior and posterior cricoid split (EAPCS) has emerged as an alternative that is nondestructive and can offer a long-lasting solution to congenital BVFP while avoiding tracheostomy.
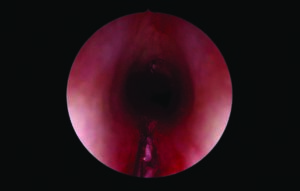

Endoscopic anterior and posterior cricoid split (EAPCS) has emerged as an alternative that is nondestructive and can offer a long-lasting solution to congenital BVFP while avoiding tracheostomy.
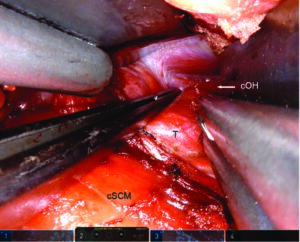
Advantages of thyroidectomy using transaxillary robotic surgery (TARS) are cosmetic, a high-definition view of structures, and a reduced risk of compressive cervical hematoma; the main drawbacks are the cost and duration of the procedure
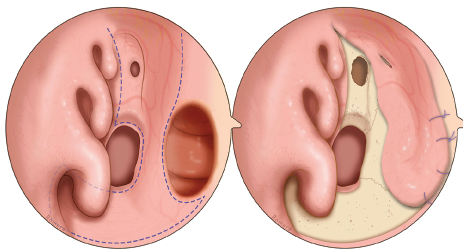
The objective of this study is to describe step by step an innovative technique to repair large septal perforations with a pure endoscopic extended AEA flap.
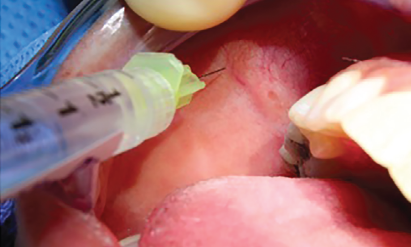
We demonstrate a novel, simplistic, and rapid approach to cannulation, dilation, and sialendoscope insertion that can be completed in an outpatient setting with the assistance of viscous lidocaine gel.
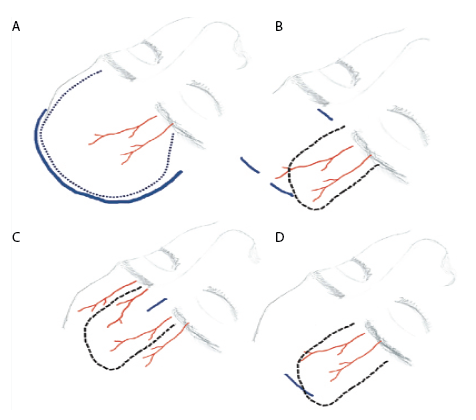
Through this endoscopic approach, glabellar incision can be avoided by performing frontal osteotomy endoscopically.
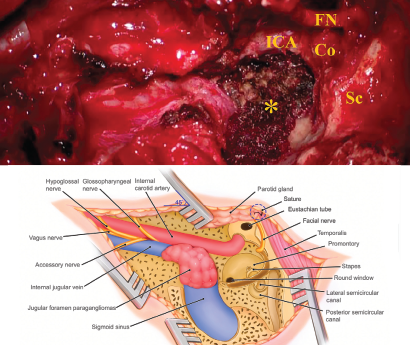
In the study, we modified Dr. Brackmann’s total anterior FN rerouting technique to achieve tension-free FN anterior transposition and explored the surgical outcomes postoperatively.
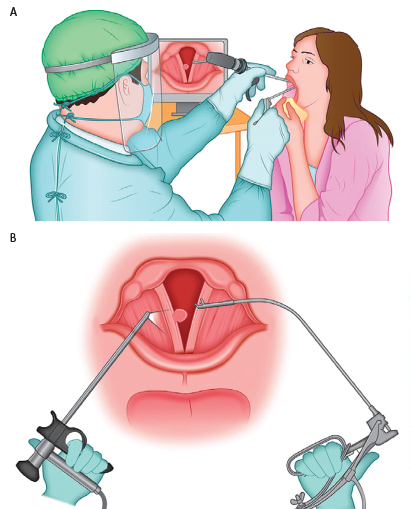
We describe a new technique for the removal of vocal fold polyp in the office setting, while simultaneously taking into consideration the safety measures proposed for the ambulatory examination of the larynx.
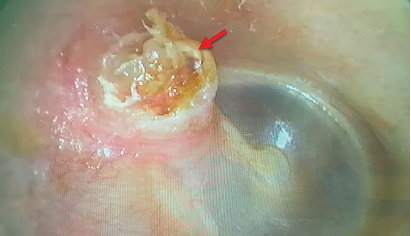
A transcanal endoscopic approach was performed with the aim of removing an epitympanic cholesteatoma without the transmastoid approach, and to reconstruct the scutum after obliteration of the epitympanum at the same time.
The anterior table defect poses a reconstructive challenge, and very few publications have described reconstructive options.

To secure the working space for any type of EES, a large sphenoidotomy with wide opening of the anterior wall of the sphenoid sinus is a crucial step.