A 29-year-old banker with a mild upper respiratory infection that’s been lingering for a week arrives at the otolaryngologist’s office with tinnitus. He had flown six days earlier and lifted at the gym five days earlier.


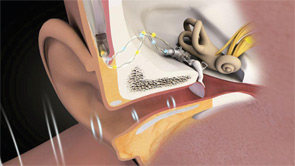
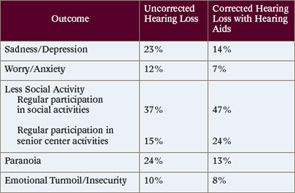
For decades, otolaryngologists have been frustrated by the refusal of some patients with hearing loss to use hearing aids. Statistics on noncompliance vary, but there is general agreement that only about 20 percent to 25 percent of Americans with treatable hearing loss use hearing aids. The problem seems to be more acute for people with mild hearing loss: A consumer survey conducted by the nonprofit Better Hearing Institute in 2009 found that fewer than 10 percent of people with mild hearing loss use amplification and that even among people with moderate-to-severe hearing loss, only four in 10 use amplification.
The question of how soon to give antibiotics to children with acute otitis media (AOM) is receiving renewed attention with the publication of two studies that show the benefit of immediate treatment over the “wait-and-see” approach recommended in the 2004 guidelines of the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAP/AAFP).
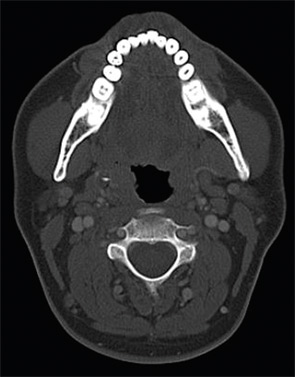
A 33-year-old white male presented with a one-year history of right-sided odynophagia. Symptoms were constant and exacerbated by swallowing. He had a history of cryptic tonsils but had not undergone tonsillectomy; his past medical history was otherwise unremarkable. There was tenderness to palpation over the right tonsil with exacerbation of symptoms. No head and neck masses were appreciated. A CT scan was obtained.
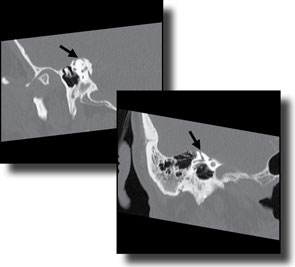
A 71-year-old male presented with an approximately 10-year history of a gradually progressive right-sided hearing loss.
Most people will experience some degree of hearing loss as they age. Statistics from the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders at the National institutes of Health (NIH) indicate that 30 percent of adults ages 65 to 74, and 47 percent of adults 75 years or older, have hearing loss.

Dizziness is a particular danger among the elderly, but extra care taken by physicians can help ease their problems and help keep older patients functioning, panelists said at the 2010 Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, held here Sept. 26-29.

The title of this session at the Triological Society’s Combined Sections Meeting held here Feb. 4-7 asked a tough question: Why are otolaryngologists still talking about pediatric tonsillitis, otitis and sinusitis?
Does the size of the dehiscence in SSCD correlate with the size of the air-bone gap? Background: Patients with superior semicircular canal dehiscence (SSCD) present with a variety of symptoms […]