A look at the prevalence, timing, and potential baseline clinical risk factors associated with patients with medically refractory chronic rhinosinusitis electing endoscopic sinus surgery.
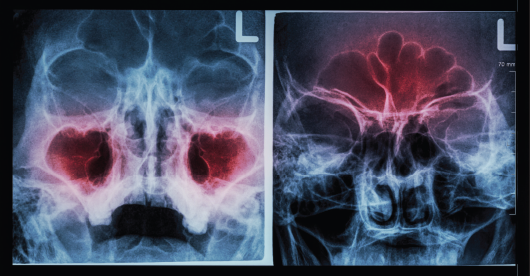
Refractory Chronic Rhinosinusitis: Medical and Treatment Options
Advanced planning can keep your income, and your clinical practice, afloat
CRS Impact on Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Not Well Known
Currently there is a lack of a validated disease specific, quality of life instrument, available to assess the impact of CRS on the pediatric CF patient population
Polyp Recurrence Still Common After ESS for CRS with Nasal Polyposis
Polyp recurrence is still common after ESS, with control of polyps up to 18 months found in approximately 60% to 70% of patients
Taste Receptor T2R38 Plays Key Role in Biocidal Defense Against CRS
When stimulated by AHLs, T2R38 elicits calcium-dependent NO production that increases ciliary beat frequency and mucus clearance.
QOL Comparison Between Surgeons Following ESS Possible
Comparison of surgeon outcomes of ESS is feasible, but must take into account a number of baseline patient characteristics
ESS Improves CRS-Related Subjective Olfactory Dysfunction
ESS improves CRS-related subjective olfactory dysfunction with greatest gains seen in those with poorer CT scores at baseline
Steroid-Releasing Implant after ESS Is Safe and Effective
Placement of steroid-releasing sinus implants in the FSO significantly reduces the need for postoperative interventions in patients with CRS who are undergoing frontal sinus surgery

What Is the Role of the Adenoid in Pediatric Chronic Rhinosinusitis?
Adenoidectomy is a reasonable first-line surgical option for pediatric patients with CRS that is refractory to medical therapy
Change in Cardinal Symptoms of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Surgery vs. Medical Therapy
For patients with CRS, endoscopic sinus surgery results in significantly greater improvement in cardinal symptoms of CRS
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- …
- 8
- Next Page »