Dr. Johnson gave the presentation at COSM 2011.

Lecturer Warns Against Overuse of CRT: Says many early-stage laryngeal cancer patients overtreated
Chemoradiation therapy (CRT) for head and neck cancer is overused at some centers in patients with early-stage laryngeal cancer, and more care should be taken not to overtreat patients with therapy that can have toxic effects, said invited lecturer Jonas Johnson, MD, at the Annual Meeting of the Triological Society, held here on April 29 as part of the Combined Otolaryngology Spring Meetings.

A Personal Spin on Migraine-Associated Vertigo Treatments: With few formal guidelines, otolaryngologists use trial and error
Physicians have noted the potential for dizziness in migraine patients since the 19th century. And yet the 21st century has so far failed to bring any unifying definition to a symptom that is frustratingly diffuse in its intensity and frequency and unclear in its origins.

Return on Recycling: Reprocessing single-use devices may lower costs, improve efficiency
The idea of reusing single-use devices may bring to mind the recent news of a Las Vegas urologist who was investigated in March for supposedly resuing single-use devices. As the Las Vegas Review-Journal reports, Dr. Michael Kaplan is accussed of reusing, but not not decontaminating, endocavity needle guides. While Dr. Kaplan’s specific case may be unique, the idea of reprocessing single-use devices is not.

Symptom Reviews: Panel discusses the nuances of otology cases

New Tool Could Aid Decisions on Elective Neck Dissection: Fast polymerase chain reaction detects sentinel lymph node positivity
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (Q-PCR) can be a valuable tool in the operating room to determine whether head and neck cancer patients should go on to elective neck dissection, researchers said here on April 29 at the Annual Meeting of the Triological Society, held as part of the Combined Otolaryngology Spring Meetings.

Neurotrophic Factors Aid Laryngeal Reinnervation: Rat study highlights potential new technique for nerve injury
Neurotrophic factors can be introduced using stem cells and, along with the plant alkaloid vincristine, can be used to selectively reinnervate the larynx in rat models, a researcher from Indiana University said here on April 29 at the Annual Meeting of the Triological Society, held as part of the Combined Otolaryngology Spring Meetings.
Targeting Headaches: Trigger release surgery an option for patients with chronic migraine
Surgically releasing specific “trigger sites” may provide long-term relief for some sufferers of chronic migraine. According to a recent study published in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 88 percent of patients who underwent surgical deactivation of targeted trigger sites reported at least a 50 percent reduction in the frequency, severity and duration of their migraine headaches five years later.

National Drug Shortage Hits ENT Surgeries: Succinylcholine, propofol and tetracaine in limited supply
When performing certain procedures, many otolaryngologists use succinylcholine, a neuromuscular blocking agent, to help them monitor the facial nerve.
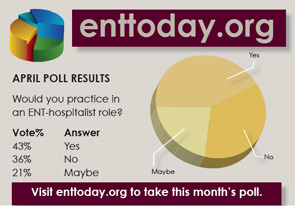
Letter: Another ENT-Hospitalist
Regarding the article, “Otolaryngologist Pioneers New Practice Model: Dr. Russell heralds hospitalist role as others ponder the concept’s staying power”…
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- …
- 39
- Next Page »